Resource Sustainability
1. Policy and Basic Approach
Securing and procuring a stable supply of resources is one of the most important functions of a trading company. However, the earth’s resources are limited, and we must therefore develop, supply, and use resources in a sustainable manner. Furthermore, in recent years there is a growing focus on the shift towards a circular economy in which reusing, reducing, and recycling limited resources enables the effective use of resources. Sojitz’s efforts to realize a circular economy are crucial, not only from the perspective of combating the global issue of climate change and contributing to the reduction of CO2 emissions from product manufacturing and waste incineration, but also because these initiatives for resource recycling create business opportunities for Sojitz.
To accomplish this aim, Sojitz has set “Resources” as one of its Materiality (Key Sustainability Issues) and pursues the development, supply, and use of sustainable resources (energy, mineral, food, water, forest, marine and other resources).We also strive to conserve resources, propose suitable energy mixes, and provide a stable supply of resources.
Furthermore, Sojitz Group’s Environmental Policy states that Sojitz will engage in curbing the use of natural resources such as energy and water, and the reducing and recycling of waste; and that it will promote initiatives for the stable supply of resources and realization of a suitable energy mix.
In the course of discussing Sojitz’s roadmap to a decarbonized society, we have identified technological and world trends for each decade and then determined our response and approach for each. In these discussions, we have positioned our contributions to the construction of a circular economy as an opportunity for Sojitz.
In April 2021, we changed the name of our Metals & Mineral Resources Division to the Metals, Mineral Resources & Recycling Division. Through this division, we will promote reforms of existing resource-related businesses and strengthen our recycling business initiatives.
2. Goals and Targets
2-1. Targets for Sojitz’s Business Activities
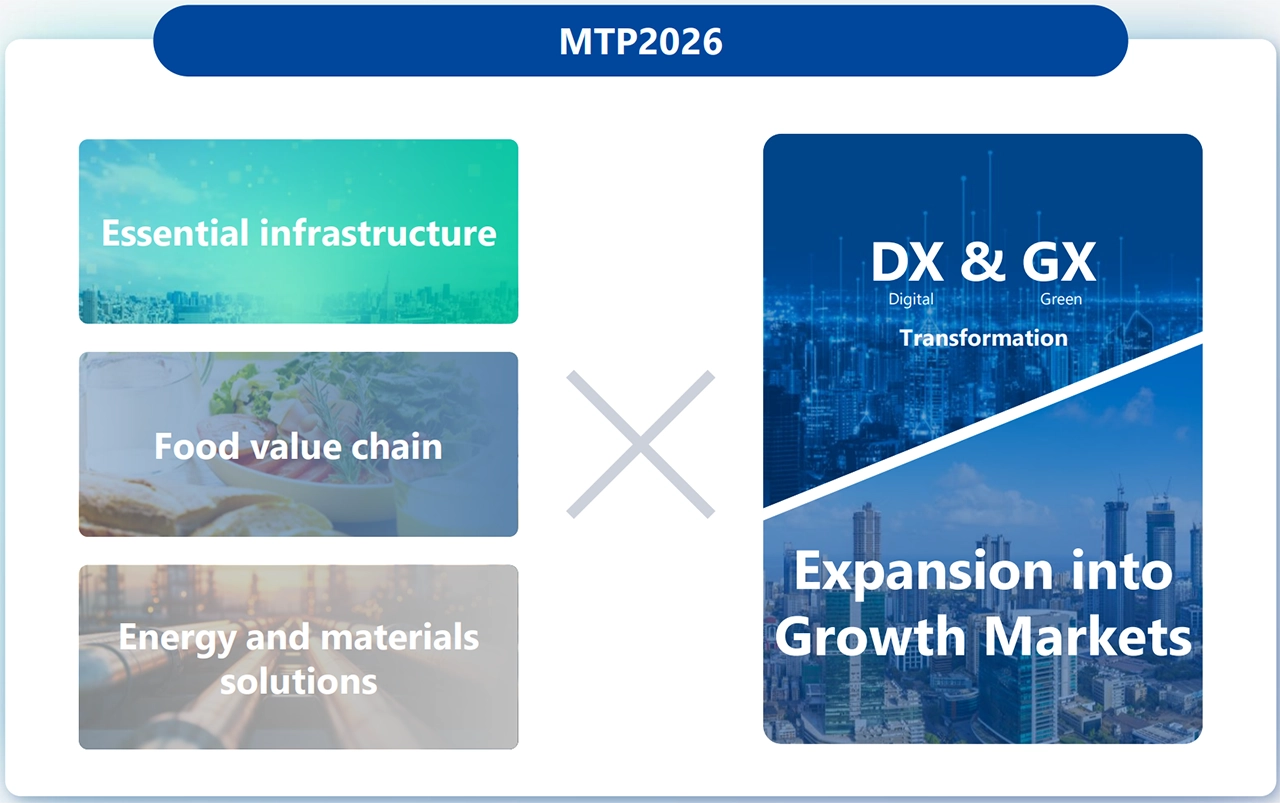
Sojitz has selected energy and materials solutions as a strategic focus area under Medium-term Management Plan 2026 announced in May 2024, and has committed to the following aims:
●We will pursue recycling and recycling-related businesses arising from shifting mass-consumption needs as well as pursue bio-materials businesses.
2-1-1. Focus Areas in MTP 2026
2-2. Targets for Office Activities
Sojitz Corporation (Tokyo HQ, Kansai Office) set a target beginning in FY2020 to continuously maintain a recycling rate of 90% or more for office waste. Sojitz achieved a rate of 95% in FY2016 and is committed to maintaining this level and further improving recycling efforts moving forward.
3. Systems
3-1. Managing Environmental & Social Risk
3-1-1. Risk Management by the Sustainability Committee / Reports Submitted to the Board of Directors (Supervisory Body)
Sojitz Group classifies and defines the many risks associated with our businesses according to our Basic Code of Corporate Risk Management( Risk Management ), and we establish a risk management policy and management plan for these risks each year, based on a resolution by the Board of Directors. Among these risks, countermeasure policy and initiatives regarding environmental and social risk (including risk related to climate change) are deliberated by the Sustainability Committee. These policies and initiatives may then be put into action following a report to the Management Committee and Board of Directors.
3-1-2. New Investment Projects
In addition to examining a project’s business plan, deliberation on all business investments and loans require projects to be analyzed and evaluated for risks to the environment (including climate change-related risks) and risks to society (such as the risk of impacting local residents and labor safety-related risks). A project’s value must be confirmed from a sustainability perspective prior to resolution.
4. Initiatives
Sojitz has set “resources” as one of its Materiality (Key Sustainability Issues), and pursues the development, supply, and use of sustainable resources. We strive to conserve resources, propose suitable energy mixes, and provide a stable supply of resources.
4-1. Participation in IT Asset Reuse and Recycling Businesses
In January 2021, Sojitz acquired a stake in TES-AMM JAPAN K.K., the Japanese branch of TES Group, one of the largest global IT asset disposition service providers. Through this investment, we look to promote the normalization of reuse and recycling of IT equipment in order to contribute to the realization of circular economies. In addition, TES Group is moving forward with the development of a lithium-ion battery recycling business that utilizes Sojitz’s network.
Sojitz also holds an in-house collection drive for unused IT equipment twice a year, and the collected devices are recycled by TES-AMM JAPAN.
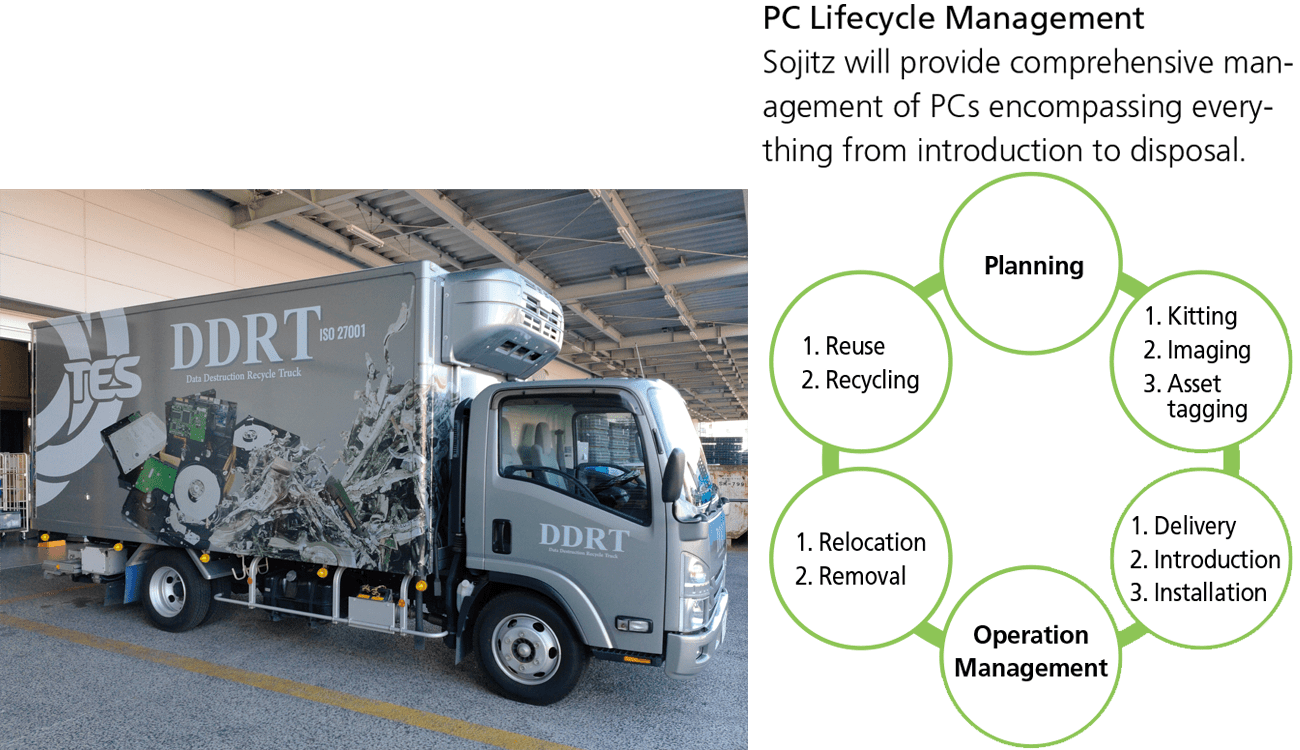
In February 2023, Sojitz acquired a 34% stake in eCycle Solutions Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of JX Metals and Canada’s largest collector and processor of e-waste (discarded household appliances and electronic devices). Sojitz and JX Metals began joint collaboration on the recycling business in April 2023.
eCycle recycles e-waste in Canada and is also developing an IT Asset Disposition (ITAD)* business. JX Metals is aiming to increase the ratio of recycled raw materials to 50% by 2040, and Sojitz has identified resource recycling as a key sustainability issue. Through this collaboration with JX Metals, Sojitz aims to enhance eCycle’s corporate value and contribute to the realization of a recycling-oriented society.
- IT Asset Disposition (ITAD): Services related to the effective use of IT assets such as discarded electronic devices and electronic circuit boards after data erasure, particularly their reuse and recycling.

4-2. Acceleration of Chemical Recycling Initiatives
-
The Chemicals Division has been accelerating initiatives in the plastic recycling market, which is expected to continue growing over the next 10 years or more, as part of its efforts to address environmental issues. Areas of focus in this regard include the capacity for processing mixed plastics comprising multiple types of plastic, the ability to use the naphtha created by refining said plastics in existing petrochemical facilities, and the potential for the production of recycled plastic with a level of quality on par with conventional plastic. With these areas of focus, we have been moving ahead with the development of waste plastic chemical recycling processes that utilize thermal decomposition oil production technologies.
-

4-3. Support for the United Nations Food Systems Summit (FSS)*1
Sojitz supports the United Nations Food Systems Summit (FSS), which was held to promote concrete actions to transform food systems*² to be more sustainable as part of the UN’s efforts to achieve all of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Sojitz will contribute to the realization of greater sustainability in food systems through its initiatives to provide a stable supply of food resources.
- The UN Food Systems Summit was a summit conceived of by United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres as an essential step to transform food systems to become more sustainable and to achieve the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Food systems refer to the series of activities involved in the production, processing, transport, and consumption of food.
- Source: Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries UN FSS
- Source URL: https://www.maff.go.jp/j/kokusai/kokusei/kanren_sesaku/FAO/fss.html
4-3-1. Goals and Targets
- Sojitz will lead the way globally in promoting the spread of MSC-certified sashimi tuna in order to pursue sustainable use of natural fishery resources. MSC certification provides proof that the seafood was caught by a responsible fishery in a sustainable manner.
- In its tuna farming business, Sojitz is committed to sustainable aquaculture and aims to maintain its certification from the Seedling Council for Sustainable Aquaculture (SCSA).
- Sojitz aims to utilize IoT and AI to industrialize tuna farming in order to improve the efficiency of its aquaculture business.
Read more
