Sojitz, Nagasaki Prefecture Sign Memorandum on Next-Generation Energy Technology Verification Project
Trials Tailored to Regional Lifestyles to be Conducted Using Huis Ten Bosch Office and Residential Facilities
Nov. 22, 2011
Sojitz Corporation signed a memorandum with Nagasaki Prefecture intended to promote industry in the environmental energy field by verifying next-generation technologies.
The key points of the memorandum are contributing to the development of next- generation technology in the environmental energy field, contributing to the development of a low-carbon society and social systems that maintain an optimal balance between electricity supply and demand, and supporting the creation of business opportunities and commercial development through collaboration with businesses in Nagasaki Prefecture.

[Solar panels installed at Huis Ten Bosch]
Sojitz and Nagasaki Prefecture are already conducting smart grid (next-generation electric transmission network) trials at Huis Ten Bosch as any 2011 Next-Generation Energy Technology Verification Project selected by the New Energy Promotion Council. With the execution of the current memorandum, Sojitz will collect various data concerning day-to-day activities at Huis Ten Bosch and other facilities and conduct trials based on various scenarios tailored to regional lifestyles in order to encourage collaboration among businesses in Nagasaki Prefecture and toward the creation of new business through implementation of these trials.
Sojitz and Nagasaki Prefecture held an initial task force conference in November and going forward will hold periodic conferences while conducting trials.
Reference Information
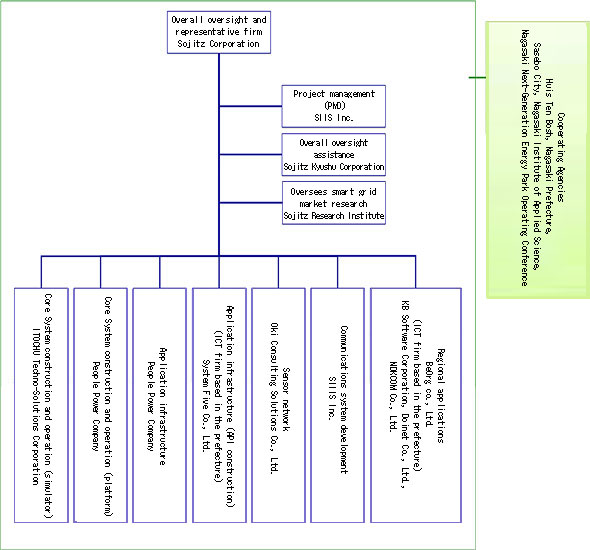
Verification Project Implementation Structure
Overview of the Trials
The trials will be conducted for three years from 2011 to 2013 with a total budget of approximately 1.5 billion yen. Approximately 500 million yen will be spent in the first year, and the national government will provide a subsidy of half up to approximately 250 million yen.
Under the trial plan, smart meters that control electricity consumption using power measurement and communications functions as well as a smart taps and motion detectors will be installed at Huis Ten Bosh, power supply and demand forecasts and target internal supply rates set, and system installation and operating costs determined to create an optimized power supply and demand model. In the first year, hardware such as smart meters and electronic displays (digital signage) will be installed mainly in offices at Huis Ten Bosh. Utilization of the optimized electric power supply and demand model ultimately developed in other regions of Japan and overseas will also be considered.
The global smart grid related market is expected to grow from approximately 940 billion yen in 2009 to approximately 5.8 trillion yen in 2020. Since the Great East Japan Earthquake in March of this year, interest has increased substantially in Japan in the development of an energy-saving, low-carbon society by employing smart grid technologies.